The shortage of energy carriers and the problems of environmental protection led to the formation of such a new scientific and technical direction as bioenergy — obtaining energy from biomass, the role of which in the energy transition is very large. In developed countries, biomass-derived fuels (bio-oil, biodiesel, biogas, methane, biohydrogen) are widely used, which significantly reduces CO2 emissions and eliminates the use of natural resources. Our research laboratory is studying the issues of using new energy sources that could not be used before due to the unresolved number of technological problems. One such source of energy is hydrogen. Hydrogen energy is one of the strategic directions for the development of the Russian economy, so we are researching the prospects for using hydrogen as an alternative to existing hydrocarbon sources.
As shown by our calculations, starting from the 2040s, hydrogen energy will play a significant role in the global fuel and energy balance, and from the 2060s, an important role, and, finally, from the 2080s, one of the key roles. Therefore, in the upcoming race, Russia cannot be a passive observer, since we are talking not only about a new source of energy, but also a wide range of industrial technologies (from new materials to control systems) that can give significant competitive advantages to those who own them.
In our opinion, the most promising method of hydrogen production is the production of hydrogen from biomass, we have developed 3 main methods for such production of biohydrogen:
- method 1 - biohydrogen production by using biogas from organic waste biomass, followed by biohydrogen production through a reformer and purification of associated CO2. Our scientific group has developed a technological instruction for obtaining biohydrogen from biomass of organic waste and experimentally obtained results on the percentage of biohydrogen in the mixture by steam reforming of biogas from biomass of organic waste;
- method 2 – biohydrogen production by thermophilic anaerobic digestion of organic waste biomass;
- method 3 – biohydrogen production from microalgae biomass and creation of a closed biocatalytic system for hydrogen production due to water biophotolysis.
All methods of obtaining biohydrogen are still under development, but in the countries of the European Union, the USA, and Japan, work is underway to obtain hydrogen from biogas and use it in the power supply of small consumers.
In 2023-2024, our research team plans to develop several technologies for generating energy from biomass (biodiesel, biogas, biohydrogen) and conduct their feasibility study. Biohydrogen is planned to be obtained by method 2, from organic waste biomass, by thermophilic anaerobic digestion. Biogas with a high content of methane is planned to be obtained from the biomass of organic waste and microalgae by anaerobic digestion under mesophilic conditions.
At this stage, the Technological instruction for obtaining 3rd generation biodiesel from microalgae biomass by the extraction method was developed (Figure 1), and the best strain of microalgae for obtaining biodiesel was selected according to the developed technological instruction.

Figure 1 - Method for producing biodiesel fuel from microalgae biomass
Reducing the cost of biodiesel production is planned through the use of the method of esterification of microalgae biomass after air purification from CO2 and industrial wastewater treatment. The scientific team plans to develop a method for cleaning industrial CO2 emissions with the biomass of microalgae of the genus Chlorella.
To clean the air from CO2 in confined spaces, a photobioreactor - a biofilter (Figure 3) was developed, where a suspension of microalgae is used as a filter material. Suspension of microalgae of the genus Chlorella purifies the air in the room, processing carbon dioxide and producing oxygen. At the same time, the photobiorector has an aesthetic appearance, does not take up much space and can be used in any closed space, for example, in an office, a classroom, and even in a small production room.
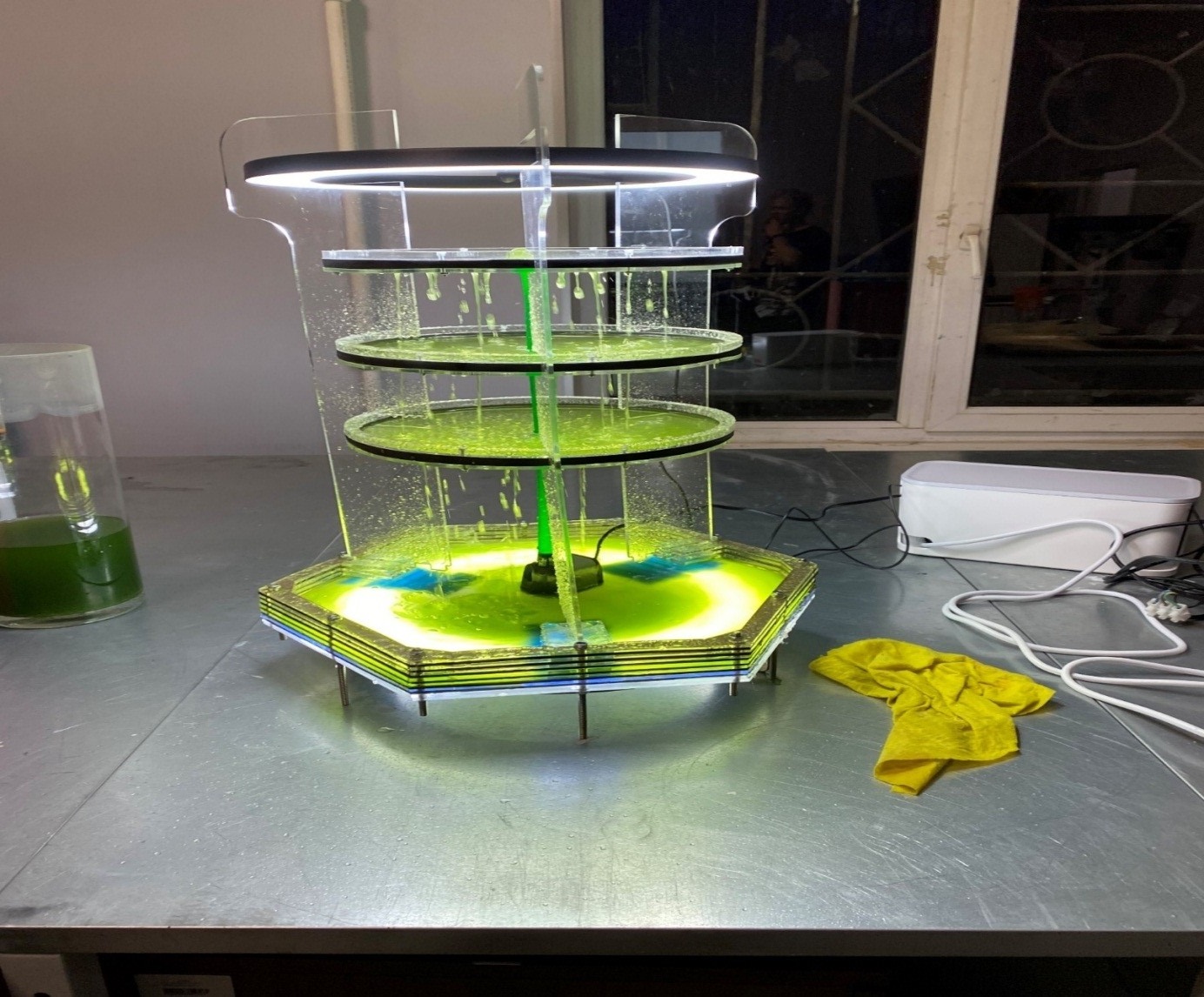

Figure 2 - Laboratory photobiorector "CASCADE", for air purification
To reduce the negative impact of CO2 emissions and other anthropogenic factors, our research team has also developed methods for the biological treatment of wastewater and soils with biomass.
For wastewater treatment, microalgae biomass was used (Figure 3), followed by the use of waste biomass as an additional energy source.

а
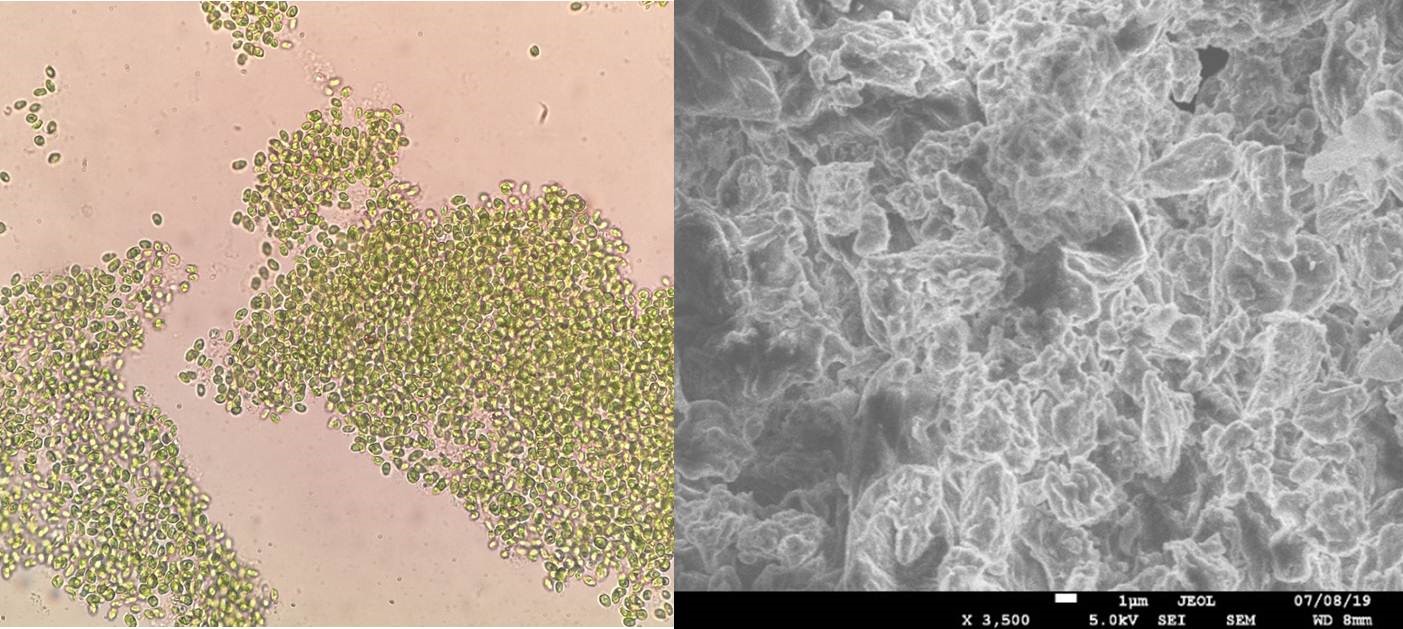
b
Figure 3 - Biomass of microalgae Chlorella kessleri (C. Kessleri): a - general view, b - cells and surface microstructure
Such an energy source will reduce the carbon footprint due to two factors: 1 - replacement of traditional energy sources with a more environmentally friendly source; 2 - by minimizing emissions of harmful substances into the environment. The results of this study are published in the article: Politaeva, N.A., Illin, I.V., Oparina, A.M., Donetskova, A.S. New energy approaches to the use of waste biosorbents of microalgae Chlorella kessleri // Povolzhskii Ekologicheskii Zhurnal, 2022, 2022(3), pp. 322–335, (WOS, Scopus), which shows:
1 - the use of biomass of microalgae C. kessleri for wastewater treatment of industrial enterprises is appropriate, in view of the high percentage of purification efficiency for copper ions - 87%.
2 - as a result of thermogravimetric analysis, it was found that during the decomposition of C. kessleri biomass after purification of the model water solution, in the temperature range of 335 - 500 °C, a strong exothermic effect occurs with a maximum of 500 °C, which allows us to give recommendations for its use as a source energy. Thermogravimetric analysis also made it possible to draw a conclusion about the content of extracted copper in the biomass of C. kessleri.
3 – it was found that the specific heat of combustion of the residual biomass of C. kessleri was 21,674 kJ/kg, which is not inferior to the specific heat of combustion of classical fuels.
Plant biomass (phytoremediants) was used for soil cleanup, which showed a high ability to extract pollutants. The results of this study are published in Ilinskiy, A.; Vinogradov, D.; Politaeva, N.; Badenko, V.; Ilin, I. Features of the Phytoremediation by Agricultural Crops of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soils. Agronomy 2023, 13, 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010127 (WoS, Q1), in which:
- empirical dependences of the content of copper, zinc, lead and cadmium in the phytomass of the studied agricultural crops on the value of the total indicator of soil pollution were obtained;
- digital models of phytoextraction of heavy metal ions by plants have been created;
- the possibility of reducing the negative impact from the complex of heavy metal ions on soils of moderately dangerous pollution with the phytomass of phytoremediant plants has been shown.



